I had the privilege recently of giving a presentation on a climate simulator called En-ROADS. What's a climate simulator? In general, a simulator is a tool designed to replicate a system's behavior to predict how it will respond under various conditions. Applied to our climate, there are numerous simulators out there that focus on different aspects to forecast future scenarios.
Why are simulators valuable? Since they aim to predict outcomes, simulators are crucial for informed decision-making. In the context of climate policies, they help address resource allocation questions, such as the investment needed for wind technology versus solar, the potential of long-duration energy storage, or the trade-offs between fusion and geothermal energy. These challenging decisions benefit from the insights provided by simulators.
So, what is En-ROADS? En-ROADS is a climate simulator that forecasts changes in the global average surface temperature. Developed initially in the mid-1990s by MIT and further enhanced by MIT, Ventana Systems, and the non-profit Climate Interactive, En-ROADS is a complex yet user-friendly tool. Its complexity lies in its numerous interconnected components, which are well-organized for ease of use.
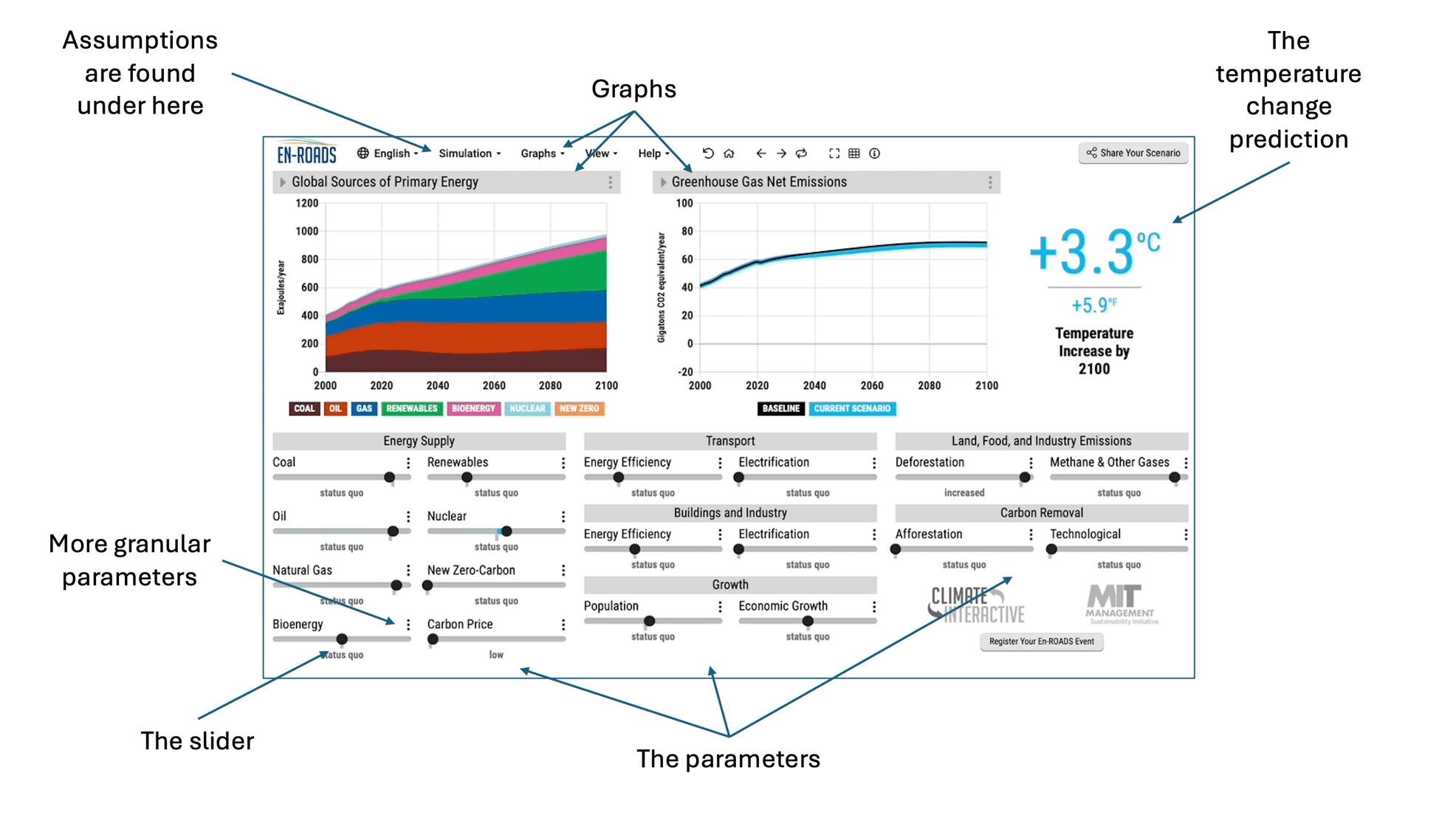
The provided figure shows the En-ROADS interface, behind which complex mathematical models operate based on one’s inputs. Available online at no cost (en-roads.climateinteractive.org), the current version of En-ROADS (version 24.6) offers145 graphs from 119 parameters under 92 assumptions for one to explore. There are two graphs and eighteen parameters displayed at any given time. Each parameter features a horizontal slider with a description underneath, allowing one to adjust settings and immediately see their impact on the graphs. The eighteen parameters shown have more detailed sub-parameters accessible via the three vertical dots.
The primary output from En-ROADS is the projected average global temperature change based on the parameter values. The secondary output are the two chosen graphs to display. By experimenting with different parameters, one can observe how their changes affect the global temperature and displayed graphs, and identify which parameters have the most significant influence. Additionally, one can explore dependencies between parameters, further aiding in resource allocation decisions to effectively combat climate change.
Despite its sophistication, En-ROADS has limitations. It treats the world as a single entity without geographic or political distinctions and does not account for human behavior. In addition, as a computer program, it also has bugs, although continuous updates address these issues.
Nevertheless, En-ROADS remains an invaluable tool for exploring climate and energy scenarios, fostering discussions on climate policy, and raising awareness about the interconnected challenges in addressing climate change.
Tags